习题1.2.13
用我们对 Date 的实现(请见表1.1.12)作为模板,开发 Transaction 的实现。
要点分析
1. Date实现
Date 的API,请见表1.1.12,课本56页,这里也给出官方网站Date类具体实现[1] :
public class Date implements Comparable<Date> {
private static final int[] DAYS = {0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
private final int month; // month (between 1 and 12)
private final int day; // day (between 1 and DAYS[month]
private final int year; // year
/**
* Initializes a new date from the month, day, and year.
*
* @param month the month (between 1 and 12)
* @param day the day (between 1 and 28-31, depending on the month)
* @param year the year
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if this date is invalid
*/
public Date(int month, int day, int year) {
if (!isValid(month, day, year)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid date");
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
this.year = year;
}
/**
* Initializes new date specified as a string in form MM/DD/YYYY.
*
* @param date the string representation of this date
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if this date is invalid
*/
public Date(String date) {
String[] fields = date.split("/");
if (fields.length != 3) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid date");
}
month = Integer.parseInt(fields[0]);
day = Integer.parseInt(fields[1]);
year = Integer.parseInt(fields[2]);
if (!isValid(month, day, year)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid date");
}
/**
* Return the month.
*
* @return the month (an integer between 1 and 12)
*/
public int month() {
return month;
}
/**
* Returns the day.
*
* @return the day (an integer between 1 and 31)
*/
public int day() {
return day;
}
/**
* Returns the year.
*
* @return the year
*/
public int year() {
return year;
}
// is the given date valid?
private static boolean isValid(int m, int d, int y) {
if (m < 1 || m > 12) return false;
if (d < 1 || d > DAYS[m]) return false;
if (m == 2 && d == 29 && !isLeapYear(y)) return false;
return true;
}
// is y a leap year?
private static boolean isLeapYear(int y) {
if (y % 400 == 0) return true;
if (y % 100 == 0) return false;
return y % 4 == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the next date in the calendar.
*
* @return a date that represents the next day after this day
*/
public Date next() {
if (isValid(month, day + 1, year)) return new Date(month, day + 1, year);
else if (isValid(month + 1, 1, year)) return new Date(month + 1, 1, year);
else return new Date(1, 1, year + 1);
}
/**
* Compares two dates chronologically.
*
* @param that the other date
* @return {@code true} if this date is after that date; {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean isAfter(Date that) {
return compareTo(that) > 0;
}
/**
* Compares two dates chronologically.
*
* @param that the other date
* @return {@code true} if this date is before that date; {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean isBefore(Date that) {
return compareTo(that) < 0;
}
/**
* Compares two dates chronologically.
*
* @return the value {@code 0} if the argument date is equal to this date;
* a negative integer if this date is chronologically less than
* the argument date; and a positive ineger if this date is chronologically
* after the argument date
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Date that) {
if (this.year < that.year) return -1;
if (this.year > that.year) return +1;
if (this.month < that.month) return -1;
if (this.month > that.month) return +1;
if (this.day < that.day) return -1;
if (this.day > that.day) return +1;
return 0;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this date.
*
* @return the string representation in the format MM/DD/YYYY
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return month + "/" + day + "/" + year;
}
/**
* Compares this date to the specified date.
*
* @param other the other date
* @return {@code true} if this date equals {@code other}; {@code false} otherwise
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (other == this) return true;
if (other == null) return false;
if (other.getClass() != this.getClass()) return false;
Date that = (Date) other;
return (this.month == that.month) && (this.day == that.day) && (this.year == that.year);
}
/**
* Returns an integer hash code for this date.
*
* @return an integer hash code for this date
*/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int hash = 17;
hash = 31 * hash + month;
hash = 31 * hash + day;
hash = 31 * hash + year;
return hash;
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code Date} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date today = new Date(2, 25, 2004);
StdOut.println(today);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
today = today.next();
StdOut.println(today);
}
StdOut.println(today.isAfter(today.next()));
StdOut.println(today.isAfter(today));
StdOut.println(today.next().isAfter(today));
Date birthday = new Date(10, 16, 1971);
StdOut.println(birthday);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
birthday = birthday.next();
StdOut.println(birthday);
}
}
}
2. Transaction
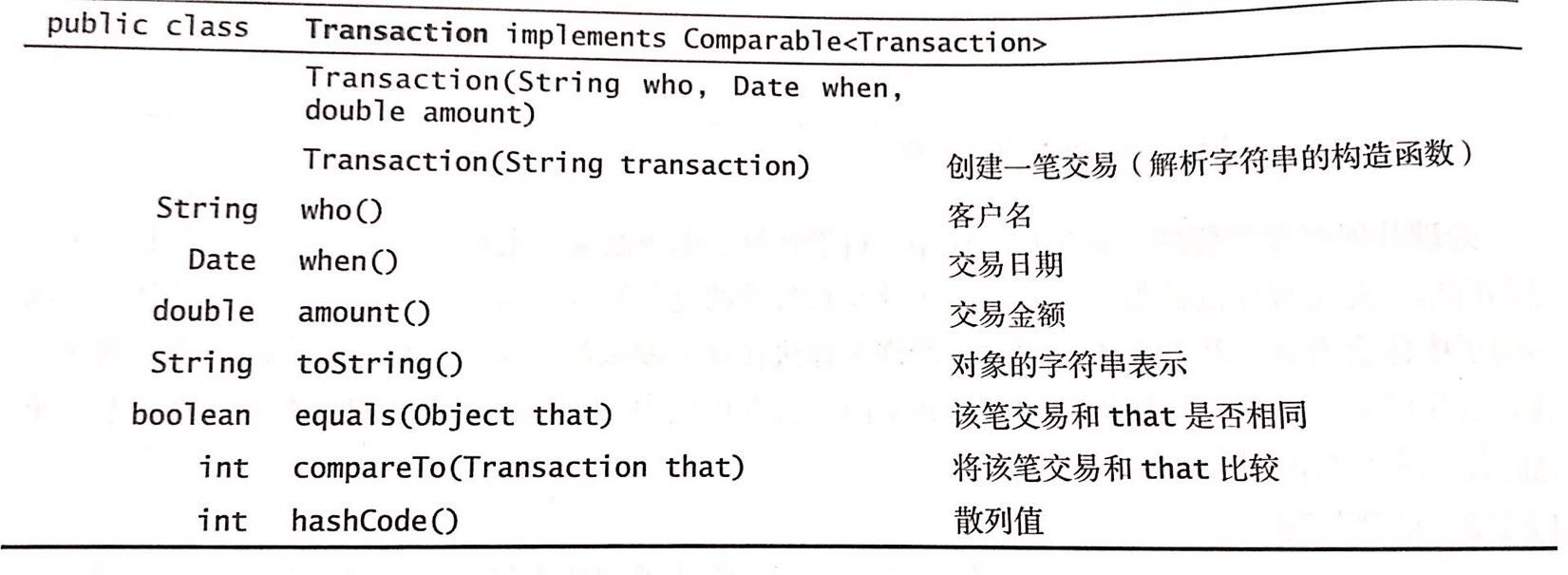
Transaction的API,请见课本48页,如下图:
我们参考Date模板的实现以及Transaction的API编写即可。
官方答案
Below is the syntax highlighted version of Transaction.java from §1.2 Data Abstraction.
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac Transaction.java
* Execution: java Transaction
* Dependencies: StdOut.java
*
* Data type for commercial transactions.
*
******************************************************************************/
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* The {@code Transaction} class is an immutable data type to encapsulate a
* commercial transaction with a customer name, date, and amount.
* <p>
* For additional documentation,
* see <a href="https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/12oop">Section 1.2</a> of
* <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class Transaction implements Comparable<Transaction> {
private final String who; // customer
private final Date when; // date
private final double amount; // amount
/**
* Initializes a new transaction from the given arguments.
*
* @param who the person involved in this transaction
* @param when the date of this transaction
* @param amount the amount of this transaction
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code amount}
* is {@code Double.NaN}, {@code Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY},
* or {@code Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY}
*/
public Transaction(String who, Date when, double amount) {
if (Double.isNaN(amount) || Double.isInfinite(amount))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Amount cannot be NaN or infinite");
this.who = who;
this.when = when;
this.amount = amount;
}
/**
* Initializes a new transaction by parsing a string of the form NAME DATE AMOUNT.
*
* @param transaction the string to parse
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code amount}
* is {@code Double.NaN}, {@code Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY},
* or {@code Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY}
*/
public Transaction(String transaction) {
String[] a = transaction.split("\\s+");
who = a[0];
when = new Date(a[1]);
amount = Double.parseDouble(a[2]);
if (Double.isNaN(amount) || Double.isInfinite(amount))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Amount cannot be NaN or infinite");
}
/**
* Returns the name of the customer involved in this transaction.
*
* @return the name of the customer involved in this transaction
*/
public String who() {
return who;
}
/**
* Returns the date of this transaction.
*
* @return the date of this transaction
*/
public Date when() {
return when;
}
/**
* Returns the amount of this transaction.
*
* @return the amount of this transaction
*/
public double amount() {
return amount;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this transaction.
*
* @return a string representation of this transaction
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("%-10s %10s %8.2f", who, when, amount);
}
/**
* Compares two transactions by amount.
*
* @param that the other transaction
* @return { a negative integer, zero, a positive integer}, depending
* on whether the amount of this transaction is { less than,
* equal to, or greater than } the amount of that transaction
*/
public int compareTo(Transaction that) {
return Double.compare(this.amount, that.amount);
}
/**
* Compares this transaction to the specified object.
*
* @param other the other transaction
* @return true if this transaction is equal to {@code other}; false otherwise
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (other == this) return true;
if (other == null) return false;
if (other.getClass() != this.getClass()) return false;
Transaction that = (Transaction) other;
return (this.amount == that.amount) && (this.who.equals(that.who))
&& (this.when.equals(that.when));
}
/**
* Returns a hash code for this transaction.
*
* @return a hash code for this transaction
*/
public int hashCode() {
int hash = 1;
hash = 31*hash + who.hashCode();
hash = 31*hash + when.hashCode();
hash = 31*hash + ((Double) amount).hashCode();
return hash;
// return Objects.hash(who, when, amount);
}
/**
* Compares two transactions by customer name.
*/
public static class WhoOrder implements Comparator<Transaction> {
@Override
public int compare(Transaction v, Transaction w) {
return v.who.compareTo(w.who);
}
}
/**
* Compares two transactions by date.
*/
public static class WhenOrder implements Comparator<Transaction> {
@Override
public int compare(Transaction v, Transaction w) {
return v.when.compareTo(w.when);
}
}
/**
* Compares two transactions by amount.
*/
public static class HowMuchOrder implements Comparator<Transaction> {
@Override
public int compare(Transaction v, Transaction w) {
return Double.compare(v.amount, w.amount);
}
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code Transaction} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transaction[] a = new Transaction[4];
a[0] = new Transaction("Turing 6/17/1990 644.08");
a[1] = new Transaction("Tarjan 3/26/2002 4121.85");
a[2] = new Transaction("Knuth 6/14/1999 288.34");
a[3] = new Transaction("Dijkstra 8/22/2007 2678.40");
StdOut.println("Unsorted");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("Sort by date");
Arrays.sort(a, new Transaction.WhenOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("Sort by customer");
Arrays.sort(a, new Transaction.WhoOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("Sort by amount");
Arrays.sort(a, new Transaction.HowMuchOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
StdOut.println();
}
}
参考资料
[1] Algs4:Date.java


请登录之后再进行评论